If you buy through our links, we may earn an affiliate commission. This supports our mission to get more people active and outside.Learn about Outside Online's affiliate link policy
Why Running at Night Feels Harder

(Photo: Jovo Jovanovic/Stocksy)
In the quiet pre-dawn hours, as I glide along the empty running path with shadows flitting past under the feeble light of the moon, I feel fast. My watch, however, tells a different story. My splits during these runs are usually slower than I’d expect based on my effort. It’s not just that I’m up earlier than usual, or running on an empty stomach. Running in the dark, it turns out, really is harder.
At least, that’s the message I take from an interesting new study by researchers at Sweden’s KTH Royal Institute of Technology, working with the Swedish military and colleagues in Slovenia. They’d noticed that soldiers on night marches seemed to burn more energy than would be expected from the physical demands of the mission, especially when wearing night-vision goggles that restrict peripheral vision. They wondered whether not being able to see forced the soldiers to alter their strides, sacrificing efficiency for stability, so they decided to test this theory.
RELATED: The Science of Being Seen At Night
Night Running and Optic Flow
The new study, published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, had 15 volunteers do a series of ten-minute treadmill walks in four conditions: with and without a 56-pound pack, and with and without a blindfold on. The treadmill was set at a comfortable pace of around 30 minutes per mile, with a laser warning system to alert them if they were about to fall off the back of the treadmill.
The results showed that oxygen use (a proxy for energy consumption), breathing, and heart rate all increased substantially when wearing the heavy pack, as you’d expect. The surprise was that they increased by nearly the same amount when adding a blindfold. Here are the graphs of those three parameters, with (circles) or without (squares) the blindfold:
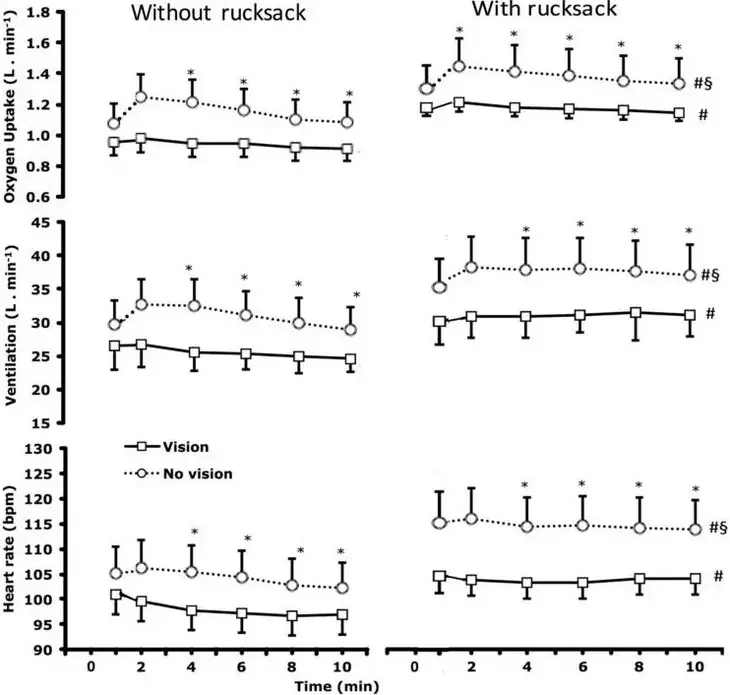
If you compare the circles on the left (i.e. blindfolded with no backpack) to the squares on the right (i.e. not blindfolded with a backpack), you see they’re almost the same. In other words, walking with a blindfold takes as much extra effort as walking with a 56-pound pack. To be precise, the backpack increased oxygen consumption by 20 percent, while blindfolding increased oxygen consumption 19 percent.
If you compare the circles on the left (i.e. blindfolded with no backpack) to the squares on the right (i.e. not blindfolded with a backpack), you see they’re almost the same. In other words, walking with a blindfold takes as much extra effort as walking with a 56-pound pack. To be precise, the backpack increased oxygen consumption by 20 percent, while blindfolding increased oxygen consumption 19 percent.
The explanation for this effect seems to be that the subjects adjusted their strides when blindfolded: their steps got 11 percent shorter and 6 percent wider, and they also lifted their feet 18 percent higher. Bear in mind that this is on a perfectly flat treadmill, so there are no bumps or potholes to avoid: this is just an instinctive response. It’s also worth noting that the effect probably isn’t just because they’re unfamiliar with the challenge of walking while blindfolded: a similar test of blind subjects found that they burned about 25 percent more energy while walking than sighted controls.
Of course, being blindfolded is significantly more disruptive than wearing night goggles, or simply being out at night in poorly lit conditions. That means the size of the effect is probably exaggerated. And walking is different from running. But it seems reasonable to assume that similar mechanisms are at work when you’re running in the dark—along with other, more subtle mechanisms like optic flow, which is the pattern of objects flowing through your vision as you move through space.
RELATED: In a World of FKTs, I Prefer to Go Slow. Really Slow.
Why Night Running Messes with Your Optic Flow
When you’re running or cycling in the dark, you can only see objects that are relatively close to you. That means that they appear in your field of vision only briefly before disappearing behind you, which corresponds to faster optic flow than you’d experience in daylight. A few previous studies, most notably those by Dave Parry and Dominic Micklewright of the University of Essex, have tried manipulating optic flow in virtual reality setups, making the scenery fly past more quickly or slowly than the speed of the treadmill or exercise bike. Sure enough, when optic flow is faster—as you’d experience in dark conditions—you feel like you’re moving faster, and any given pace feels harder.
There’s an interesting corollary to these findings about optic flow, as Parry explained to Runner’s World’s Scott Douglas back in 2012. “Running in an environment where most of the visual reference points you can see are close by, you experience a greater sensation of speed than when in an environment where your reference points are far away,” he said. That means running through a forest or through city streets will likely feel faster than running across an open field.
Ever since reading about those optical flow results, I’ve dismissed the gap between my actual and perceived pace during night runs as a quirk of how my brain estimates effort. During most of my runs, that gap doesn’t matter—but if I’m trying to do a tempo run or hard workout before sunrise, the slower pace can be a bummer. So I’ll take the new Swedish results as reassurance that night running might really be physiologically harder, not just a brain error—and if that’s what it takes to avoid tripping in the dark, I’ll accept the trade-off.
For more Sweat Science, join me on Twitter and Facebook, sign up for the email newsletter, and check out my book Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human Performance.